Welcome to
Explore Automotive, in this blog we learn about different functions of
automobile chassis components.
As we say Definition of chassis so let us know about it ,the name ‘Chassis’ is a French term that was initially used to denote the frame or main structure of the vehicle. The chassis frames includes all the major units that are necessary to propel the vehicle, guide its motion, stop it and allow it to run smoothly over uneven surfaces.
Automobile chassis is the main mounting member for all
the components including the body. And it is also known as the carrying unit.
Functions of Chassis
The
functions of the chassis includes
1) Chassis
carries the weight of the vehicle and its passengers, and goods in case of
cargo vehicles
2)
Withstanding the engine and transmission torque and thrust stresses, as well as
accelerating and braking torque,
3)
Withstanding the centrifugal force while taking a turn and
4)
Withstanding the bending load and twisting due to the rise and fall of the
front and rear axles.
Different
components of automobile chassis system
Here are some major components of automobile and their functions listed below:
1) Frame
Chassis frame is the basic frame work of an automobile which supporting all the parts of the automobile attached to it. Chassis frame is made up of the material that is drop forged steel.
Different types of loads applied on the
Chassis Frame
(i) Stationary
loads, it means that the loads of permanent attachment like all the parts of
the chassis, body of the vehicle.
(ii) The loads
which are caused by sudden accidents, head on collusions etc.
(iii) The
loads which are caused by irregular and overloading of the vehicle
(iv) Short
duration loads, the load comes on the vehicle while turning, braking.
(v) Momentary loads, this type of loads applied on the vehicle while quick acceleration, sudden braking etc.
(vi) The loads that are applied while crossing the roads of irregular and uneven surfaces
2) Radiator
The main
function of the radiator is to cool down the water that received from the
engine.
The
radiator has three main parts which are as follows:
(i) Upper
tank, (ii) Lower tank and (iii) Tubes.
Hot water
which is present in the upper tank, which comes from the engine, flows
downwards through the tubes. And that time, the heat contained in the hot water
is conducted to the copper fins which are provided around the tubes. An
overflow pipe, connected to the upper tank that permits excess water or steam
to escape.
There are
three types of radiators:
(i) Gilled
tube radiator,
(ii)
Tubular radiator and
(iii)
Honey comb or cellular radiator
Gilled
tube radiator: This type of radiator is the oldest type of radiator and it is
still in use. In this radiator, water flows from inside the tubes. And each
tube having a large number of annular rings or fins which are pressed firmly
over its outside surface.
Tubular
radiator: The one slightly difference in a gilled tubes radiator and a tubular
that is in this case there are no separate fins for individual tubes. The
radiator having vertical tubes which passes through thin fine copper sheets
which runs in horizontal manner.
Honey comb
or cellular radiator: This type of cellular radiator consists of a large number
of individual air cells which are surrounded by the water. In this type, the
clogging of any passage or area affects only small amount of parts of the
cooling surface. It means that in the tubular radiator, if one tube becomes
clogged, the cooling effect of the entire tube is lost.
3) Engine
An engine
is the complex unit in which different components are assembled together, and
fuel is burned by the engine to produce power or energy. The main function of engine is to converts
chemical energy (heat energy) into mechanical energy, which is then utilised
for the movement of vehicle.
When the fuel is burned inside the engine, it is called an Internal Combustion (IC) engine, and when the fuel is burned externally and the produced steam is used for the movement of machine that is called as an External Combustion (EC) engine. This is the main difference between IC engine and EC engine.
In an IC
engine, the reciprocating motion of the piston inside the cylinder is converted
into the rotary motion of the crankshaft and the produced the power which is
then transmitted to move the vehicle.
In case of
a rotary engine or Wankel engine, the rotor rotates and completes the process
of combustion and produces the power that generated power helps to the movement
of vehicle.
4) Clutch
Clutch is
a mechanism placed between the flywheel and gearbox which enables the rotary
motion of one shaft to be transmitted, when desired. The axes of both the driving
shaft and driven shaft are coincident to each other.
Functions of clutch
Main
function of clutch is that to disconnect the engine power from the gear box as
per required, under the following conditions:
(i) To
start the engine and warm up the engine;
(ii) To engage first and second gear to start
the vehicle from standstill condition;
(iii) To
facilitate while changing the gear as per requirement; and
(iv) To disconnect
the transmission line from the engine to stop the vehicle after application of the
brakes.
(b) To
allow the engine to take up the load gradually without any sudden shock or jerk
occur.
5) Gearbox
We require different gear ratios in the gear box or transmission system to enable the vehicle to move at different speeds according to the road conditions.
At the time of starting the vehicle, the maximum amount of torque is available on the flywheel, for that condition low gear ratio is selected for the movement of the vehicle.
As the speed of the engine increases, the amount of torque gets reduced on the flywheel and it is required to select higher gear ratio for faster vehicle movement.Functions of a gear box
(i) To
provide variations in the leverage or torque ratio between the engine and the
road wheels as per required based on the road condition.
(ii) The
transmission also provides a neutral position so that the engine and the road
wheels are disconnected even with the clutch is in the engaged position.
(iii) It
provides a function to reverse the vehicle by selecting the reverse gear.
6)
Universal Joint and Propeller shaft
Universal
joints:
One or two universal joints are used in the vehicle basically depending upon the type of rear axle drive used in that particular vehicle.
The universal joints serves in
the up and down movements of the rear axle when the vehicle is in running
condition.
Propeller Shaft:
Propeller
shaft is a shaft which transmits the power from an engine to the wheels of the
vehicle. Propeller shaft is a hollow tubular shaft which consists of following
parts.
(i) Shaft:
Shaft mainly carries torsional stresses which produced due to twisting. It is
usually made of tubular cross section.
(ii) Slip
joint: Depending on the type of drive, one slip joint may be there in the
shaft. This joint works for adjusting the length of the propeller shaft when
demanded by the rear axle movements.
7) Final
Drive
Final drive is functioning for the power transfer from propeller shaft to rear (or front if automobile is front wheel driven) axles and then to the wheels.
Final drive that turns the propeller shaft motion at right angle to drive the rear axle. The final drive is composition of a bevel gear that also called as a pinion and crown wheel.
The bevel pinion is connected with the propeller shaft. And the pinion is in mesh with the crown wheel which is a part of differential. Final drive gives fixed speed reduction.
And because of the crown wheel has more number of teeth and connected to the rear axles and bevel pinion has less number of teeth. For the final reduction in speed, two types of gears can be used.
One of them may be use of bevel gears
and another may be worm and worm wheel. Worm and worm wheel combination
provides a large reduction without employing larger gears and it is strong
also.
Slip Joint: The rear axle housing with the wheel and differential is attached to the frame of an automobile through the springs.
As the vehicle moves over uneven surface road condition, this time whole assembly moves up and down due to expansion and compression of the springs. This phenomenon changes the length of propeller shaft because it is connected to differential and gear box.
And this is main
function of a Slip joint that allows for the change in length of propeller
shaft. When the spring is compressed propeller shaft shortens and when the
spring is expanded, propeller shaft returns to its original length.
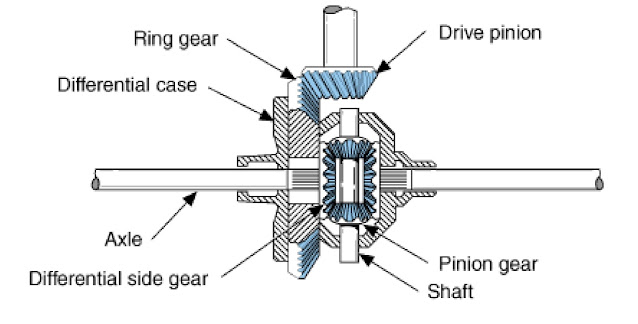
8) Differential
When a vehicle such as a car or truck takes a turn, at that time the outer wheel turns faster than the inner wheel. So, there is a relative movement takes place between the inner and the outer wheel.
The function
of the differential is that to permit the relative movement between the
inner and outer wheels when vehicle initiates to take a turn.
The torque transmitted to each of the rear wheel is equal in this case, although their speed is different. The differential is made up of a system of gears that connects the propeller shaft and the rear axles.
Differential is a part that is
placed in the inner axle housing assembly. This assembly consisting of
differential, rear axles, wheels and bearings.
There are
three types of differential which are as follows:
(a)
Conventional type differential,
(b)
Non-slip or self locking type differential, and
(c) Double
reduction type differential.
Conventional Type:
Conventional type differential delivers same torque to each rear wheel. If any
one of the wheels of a vehicle that slips due to any reason the wheel does not
rotate and vehicle does not move.
Non-slip or Self Locking Type: Non-slip
or self locking type differential overcomes the drawback which comes in
conventional type differential. Its construction is similar to that of conventional
type differential. But one thing that separates is that, two sets of clutch
plates are provided additionally in this type. Also, the ends of planetary
shafts are leaves as loose condition with notches are provided on the
differential cage.
9) Half
Axle
Rear axle functions that transmits the power from differential to the wheels so that the vehicle can move. Rear axle is not a single piece but it is in two half parts which are connected by means of the differential.
Each part of the rear axle is divided into two half that is called the half shaft. Outer end of the rear axle, each half axle carries the wheel while inner end is connected to sun gear of the differential. In vehicles which employ rear wheel drive, rear wheels are the driving wheels.
However, in front wheel drive vehicles, front wheels are the
driving wheels. Rear axles and the differential both are completely enclosed in
a housing to protect them from the dust, dirt, water and any possible damage.
Functions of Rear Axle
(i) The
main function of rear axle is that to transmit the power from differential to
the wheels.
(ii) And
also supports to carry the weight of an automobile.
10) Wheels
and Tyres
Wheel
The wheel is an important component which gives primary suspension to the vehicle. Wheels of a vehicle are mounted on a hub and consist of parts like rim, tyre and tube.
The wheels provide support the weight of the vehicle and also protect it from
road shocks. All the four wheels of the vehicle must resist the braking
stresses and withstand the side thrust. A wheel must be light in weight and
easily removable at the time of maintenance.
Functions of the wheel
(i) To
grip the road surface.
(ii) To
balance dynamically it means when the vehicle is in motion and statically means
when the vehicle is at rest condition.
(iii) To
withstand the weight of the vehicle.
(iv) To
absorb road shocks.
Tyre
The tyre is mounted on the wheel rim that carries the vehicle load and provides a cushioning effect to the whole structure. Tyre helps to produce minimum noise, while the wheel take turns on the road.
Tyres also resist the tendency for the
vehicle to oversteer. Tyres should have good grip while accelerating and
braking the vehicle on both dry and wet roads.
Functions of Tyre
(i) To
transmit the power from the engine through gear box, propeller shaft and rear
axle to the ground with which the vehicle moves.
(ii) The
treads made on the tyres grip the road for better traction.
(iii) To
carry the load of the vehicle.
(iv) To
absorb minor road shocks.
(v) To
reduce vibration to some extent.
11) Suspension
System
Suspension denotes that the system of springs, shock absorbers and linkages that connects a vehicle body to its wheels.
The suspension system gives a dual purpose that
contributing to the vehicle’s road holding or handling and braking for the
safety and also gives driving comfort, and keeping the vehicle occupants
comfortable and well isolated from the road noise, bumps and vibrations that
occurs while riding.
Functions of suspension system
The
functions of a suspension system are given as follows:
(i)
Suspension system provides safeguard to the occupants against road shocks and
provide riding comfort to the passenger.
(ii) Suspension
system isolate the structure of the vehicle from the shock loading and
vibration due to irregularities of the road surface without impairing its
stability.
(iii)
Suspension system helps to provide the proper height to the body structure of
the vehicle as well as to bear the torque and braking reactions.
(iv) To
minimise the effects of stresses produced by the road shocks on the mechanism
of the motor vehicle and provide a cushioning effect.
(v) To
keep the body perfectly in level while travelling over rough uneven ground,
i.e., the up and down movement of the wheels should be relative to the body.
12) Electrical or Electronic System
In current
scenario, all the vehicles run with the help of electrical and electronic
system, and because of that, this system plays an important role in the
functioning of an automobile.
Electrical
and Electronic systems consists the sub systems which are as follows:
(i) Starting
system: For the
starting of an engine, the starting motor placed which is driven by
means of the current taken from the battery.
(ii) Ignition
system: The function
of the ignition system is that it produces a spark by using spark plug
which is placed in the engine combustion chamber at the end of the compression
stroke.
(iii) Generating
or charging system: The function
of the charging system in an automobile is to generate, regulate and supply
the electrical energy to charge the battery.
(iv) Lighting
system: This system consists of various types of lighting
used during the vehicle in running condition, such as head lights, tail lights,
left and right indicators, parking light, cabin light, panel board lights, fog
lights, brake lights, reversing light, etc.
(v) Electric
and electronic system also provides connections
for other accessories.
13)
Steering System
The steering system permits that the driver can easily control the car on a straight road and turns right or left as per requirement. The steering mechanism includes that a steering wheel, which the driver controls, a steering gear, which converts rotary motion of steering wheel in to straight line motion and steering linkages.
In latest cars, the manually operated steering system is
assisted by the power such as hydraulic or electric means and is called that
power steering. The electric power utilised from the battery or hydraulic power
is used.
Functions of a Steering System
(i) This
system is used to turn the vehicle as per the will of the driver.
(ii) It
converts the rotary motion of the steering wheel into angular displacement of
the front wheel.
(iii) It
multiplies the effort of the driver to ease operation.
(iv) It
absorbs road shocks and prevents them from reaching the driver.
(v) It
provides directional stability to the vehicle when moving in a straight (ahead)
direction.
(vi) It
provides perfect steering condition, i.e., perfect rolling motion of the wheels
at all times.
(vii) It
facilitates straight ahead recovery after completion of turn.
(viii) It
controls the wear and tear of the tyre.
14)
Braking System
In Automobiles brakes function as very important role in slowing down the vehicle and stopping of the vehicle as and when required by the driver.
Mainly there
are two types of brakes are, (i)
Internal expanding (ii) External contracting type. Different types of
brakes are used which are available in the market in different vehicles as per
the requirement.
According
to application, there are different types of brakes which are as follows:
Mechanical brakes,
Hydraulic air brakes,
Vacuum brakes,
Functions
of Brakes
(i) To
travel smoothly and safely even in heavy flow of traffic by controlling the
movement of the vehicle.
(ii) To
slow down or to stop the vehicle as and when required.
(iii) To
control the vehicle when the vehicle is rolling down on a slope road down ward.
























As a student of automotive engineering have learnt a lot on this page for sure , it's awesome thanks
ReplyDeleteNice information, thanks for sharing. If you are looking for top dollars for an old car, We are literally the Top Car Buyer in Brisbane company- with hands-down the most efficient, quickest, and highest paying car buying service. You won’t help but simply fall in love with our team. They will leave you wanting to get rid of the old and flaunt a new car every now and then.
ReplyDeleteNice information, thanks for sharing. If you are looking for top dollars for an old car, We are literally the Top Car Buyer in Brisbane company- with hands-down the most efficient, quickest, and highest paying car buying service. You won’t help but simply fall in love with our team. They will leave you wanting to get rid of the old and flaunt a new car every now and then.
ReplyDelete